Physical Topology: -The arrangement of a network that comprises nodes and connecting lines via sender and receiver is referred to as network topology.
Topology is derived from two Greek words topo and logy, where topo means ’place’ and logy means 'study'. In computer networks, a topology is used to explain how a network is physically connected and the logical flow of information in the network. A topology mainly describes how devices are connected and interact with each other using communication links.
A) Mesh Topology:
- In a mesh topology, every device is connected to another device via a particular
channel.
Every device is connected with another via dedicated channels. These channels are known as links.
- Suppose, N number of devices are connected with each other in a mesh topology, the total number of ports that are required by each device is N-1. In Figure 1, there are 5 devices connected to each other, hence the total number of ports required by each device is 4. A total number of ports required=N*(N-1).
- Suppose, N number of devices are connected with each other in a mesh topology, then the total number of dedicated links required to connect them is NC2 i.e. N(N-1)/2. In Figure 1, there are 5 devices connected to each other, hence the total number of links required is5*4/2 = 10.
B) Star Topology:
- In star topology, all the devices are connected to a single hub through a cable. This hub is the central node and all other nodes are connected to the central node. The hub can be passive in nature i.e., not an intelligent hub such as broadcasting devices, at the same time the hub can be intelligent known as an active hub. Active hubs have repeaters in them.
C) Bus Topology:
- Bus topology is a network type in which every computer and network device is connected to a single cable. It transmits the data from one end to another in a single direction. No bi-directional feature is in bus topology.
- It is a multi-point connection and a non-robust topology because if the backbone fails the topology crashes.
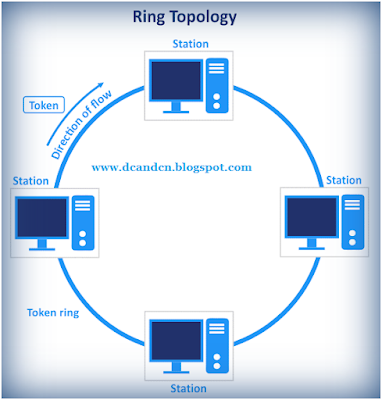
D) Ring Topology.
- In this topology, it forms a ring connecting devices with exactly two neighboring devices.
- A number of repeaters are used for Ring topology with a large number of nodes, because if someone wants to send some data to the last node in the ring topology with 100 nodes, then the data will have to pass through 99 nodes to reach the 100th node.
- Hence to prevent data loss repeaters are used in the network.
- The transmission is unidirectional, but it can be made bidirectional by having 2 connections between each Network Node, it is called Dual Ring Topology.
E) Tree Topology.
- This topology is the variation of the Star topology. This topology has a hierarchical flow of data.
Cabling (Networking)
- Cabling is the set of wires made of either copper or glass that is used to connect computers and other network components to enable them to communicate, thus forming a network of computers.
- Coaxial—›CoaxiaI cables, commonly called coax, are copper cables with metal shielding designed to provide immunity against noise and greater bandwidth. Coax can transmit signals over larger distances at a higher speed as compared to twisted pair cables.
Structure of Coaxial Cables
Coax has a central core of stiff copper conductors for transmitting signals. This is covered by an insulating material. The insulator is encased by a closely woven braided metal outer conductor that acts as a shield against noise.
Optical Fibers:-
Optical Fibers An Optical Fiber is a cylindrical fiber of glass that is a hair-thin size or any transparent dielectric medium.
The fiber which is used for optical communication is waveguides made of transparent dielectrics.
The main element of Fiber Optics:
1. Core:
It is the central tube of very thin size made of optically transparent dielectric medium and carries the
light transmitter to receiver and the core diameter may vary from about Sum to
100 um.
2. Cladding:
It is the outer optical material surrounding the core having reflecting index lower than the core and cladding helps to keep the light within the core throughout
phenomena of total internal reflection.
3. Buffer Coating:
It is a plastic coating that protects the fiber made of silicon rubber. The typical diameter of the fiber after the coating is 250-300 um.
UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair).
- UTP is an unshielded twisted pair cable used in computer and telecommunications mediums. Its frequency range is suitable for transmitting both data and voice via a UTP cable. Therefore, it is widely used in the telephone, computers, etc.
- It is a pair of insulated copper wires twisted together to reduce noise generated by external interference. It is a wire with no additional shielding, like aluminum foil, to protect its data from the exterior.
STP (Shielded twisted pair):
- A shielded twisted pair is a type of twisted pair cable that contains an extra wrapping foil or copper braid jacket to protect the cable from defects like cuts, losing bandwidth, noise, and signal interference. It is a cable that is usually used underground, and therefore it is more costly than UTP.
- It supports higher data transmission rates across long distances. We can also say it is a cable with a metal sheath or coating that surrounds each pair of the insulated conductors to protect the wire from external users and prevent electromagnetic noise from penetrating.
Bbelldad Twlatnd Pair (8TP)


















Understanding network cabling types like coaxial and OFC is crucial before you setup rookie sideloader for optimized connectivity. A well-structured physical topology ensures smoother data flow and fewer setup issues.
ReplyDelete